Dr. O. FERRER-ROCA & A. SOSA PEREIRA
To analize the minimum requirements in a Telemedicine service or device we should know:
An in those which already available which are the European or international standards , rules and legislation. Also a basic knowledge of the Standardization committees is required.( in Annex I )
1.- Type of Information to be sent
1.1 AUDIO
1.2 DATA
1.3 FAX
1.4 STILL IMAGES
Still image standards:
Other image formats :

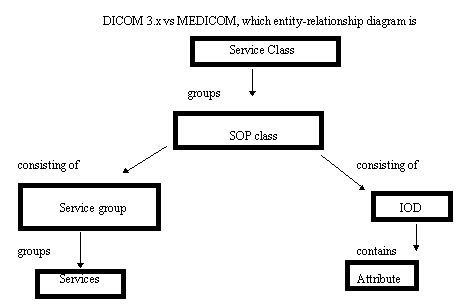
One IOD ( Information Object definition ) allow the
representation of entities ( class of real world objects that
share the same properties ) Each attribute is a different
propriety of the entity.
A SOP class ( Service -object pair ) is the union of an IOD with
the applicable service group.
A Service Class specification define a group of one or more SOP
classes related with a specific function ( for exaple functions
related with a remote storage ( Storage Service Class ) or with
an object search ( Query/retrieve service class )
1.5 CSCW ( Computer supported cooperative work ) which is a distributed application that can be concurrently used by a group of interactive users. Is an intermediate situation between data and image transmision. Require:
- Representation of data objects and relation between them
- DICOM
- SGML
- - HTML
- - HyTime
- Presentation of data of the users and synchronization between them
- MHEG ( Multimedia &Hypermedia Information object expert group )
- WYSIWIS ( What You See Is What it IS )
1.6 VIDEO
- CCITT H320 the umbrella specification for Videotelephony
- CCITT H324 for analog lines ( Visual Telephone over PSTN )
- CCITT H 261,262,263 compress video data provided by software and hardware ( Videocodecs ) for audiovisual services at px64Kb/s
- H231 Videomultiplexing for multipoint connection (MCU)
- Image format :
- CIF ( 288x352 )
- QCIF ( 144x 176 )
- CCIR 601 ( 720x576 )
- CCITT H323 For Internet protocols. Packet networks based on TCP/IP and Internet
- MPEG ( Isomotion Picture Expert group ) versions 1,2,3.
- NTSC,SECAM,PAL
- HDTV ( High definition TV )
- VBR ( Variable bit rate coding video )
2.- Types of communications and networking
2.1 NetwoRking architecture : The ISO model is the basic reference model to assure a total interconnection between systems. This does not mean that the systems will be really compatible but at least that they contain specifications that allow compatibility with appropiate interfaces.
The 7 levels of the ISO model include :
Level 1 Physical Layer : RS-232,RS-449, V37,V17,V28, DICOM 20 pin connector etc...
Level 2 Data Link Layer : rules for transmission and reception through the physical layer
HDLC( data link central ) ; LAN controles and access methodos to Ethernet ( IEEE802.3 ), Troken Bus ( 802.4 ), Token ring ( 802. 5), Fast Ethernet, ATM and Frame relay; Interface for lan controles such as NDIS ( network Drivers Interface specification )
Level 3 Network level. Protocols that assure the opening and mantainance of connection in the network
IP ( Internet Protocol ); X.25 ; IPX ( Internetwork packet exchange ),VIP ( Vines Internet protocol)
Level 4 Transpor Level .High control level to transport information between systems including sofisticated utilities for error control, priority, security etc..
TCP ( Transmission control protocol ), UDP ( User datagram protocol ), SPX ( sequential packet exchange ), VICP-VINES, NetBios/NetBeui
Level 5 Sesion Level .Dialog between systems to know what the other are doing H231, Apple-Talk
Level 6 Presentation L. The norms used to define the applications that produce transfer files,message .. TELNET, Unix virtual terminal ; fTAM file transfer accesionel management; DTP ,distributed transaction process, X.400 management mesages, EDIFACT sintax rules,; e-mail : SMTP ( simple mail transport protocol ), POP3 ( post office protocol ), MIME ( multipurpose internet mail extension ), IMAP4 ( internet message access protocol )
Level 7 Application layer
2.2 POTS ( see Chapter 4 ) Public Old transmission system
2.3 ISDN ( see Chapter 4 ) Integrate service digital network
2.4 ATM. Asynchronous transfer mode networks
Most national ATM backbones are connected in a pan-European ATM backbone network
Speed from : 2Mbps to 155 Mbps
Other Fixed networks are : SMDS ( Switched Multimegabit Data Service ) and Frame Relay
2.5 GSM
Support transmission fax/data at 9600 bps. Networking of various channels is possible ( Nokia )
Transmission mode can be:
- transparent ( negotiations and error corrections to match the settings )
- non transparent ( equal settings are required )
A GIWU ( Gateway InterWorking Unit ) such as the Ericsson, support compatibility towards PSTN modems : V.21, V.22, V.22bis, V.32 and V.42
2.6 Satellite :
Satellites services, can be divided into
- Private VSAT ( Very small antenna Terminals )
- Structure of the network assure confidentiality ( no access to unauthorised users )
- Different satellite networks are not compatible, some have user agreements
- Low cost antenas ( 1,8 diameter)
- In general point to point; multipoint is also available
- Public INMARSAT ( International Maritine Satellites )
- Are public networks directed by PTTs.
- Have 4 standards :
- Standard A.- Analog at 9,6 Kbs. Data up to 64 Kbs
- Standard B.- Digital at 9,6 Kbs. Data up to 64 Kbs
- Standard C.- No voice. Data up to 600 Kbs
- Standard D.- 4,8 Kbs. No voice. Data at 2,4 Kbs
Quality of displays are mandatory in order to assure :
* User friendly devices
* Diagnostic capabilities
On Image-based Telemedicine services, teleradiology is the only one that have standardized their display devices ( see Chapter 3 ) according to their applications :
a) Small matrix applications 0.5 K x 0.5K x 8 bits devices
b) Large matrix applications 2K x 2K x 8 bits devices.
Noticed that although images could have a wider dinamic range ( 12 bits ) the limit due to signal/noise ratio of displays devices is 10 bits and limit of human eye is 6 bits.
Display devices according the technology can be : Analog, Digital, Laser displays
3.1 Analog
3.2 Digital
3.3 Laser displays.
The latter degenerations of displays ( Scheider technology ) that allow...
4.- Human and organizational factors.
Chapter 7 introduce the
outstanding importance of the organizational enviroment, the role
of the Studio in the delivery of services and the importance of
human impact in an efficient Teleservice.
Succed in Telemedicine applications also include economic
analysis but particularly the hability to design mission oriented
telemedicine policies ( see Chapter 10
).
As an example of the mission oriented policies we may include the
psychiatry individual support at distance that require:
- Special islotation and privacy for patient and psychiatrist.
- Distant Videocamara monitoring for emotional control and detection
- Smooth notbreaking telecommunication systems that assure an adecuate progressive psicological transfer.
5.- Legal aspects ( see Chapter 8 & 9 )
Topics related with the legal enviroment that may facilitate the development of Telemedicine are:
Part or total reproduction not allow without permission
Revisado: lunes, 26 mayo 1997.
Con el soporte informático y de comunicaciones
del CICEI, Universidad
de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria